Ant Bites: Identification, Treatment, and Prevention
Encountering ant bites is an unfortunate, yet common, experience for many. From a minor nuisance to a significant health concern, understanding how to identify, treat, and prevent ant bites is crucial. This article provides a comprehensive guide to navigating the world of ant bites, offering insights into various species, their venom, and effective strategies for managing their effects.
Identifying Ant Bites
Distinguishing ant bites from other insect bites is the first step in proper management. While some ant bites may seem innocuous, others can cause significant pain and allergic reactions. Here’s what to look for:
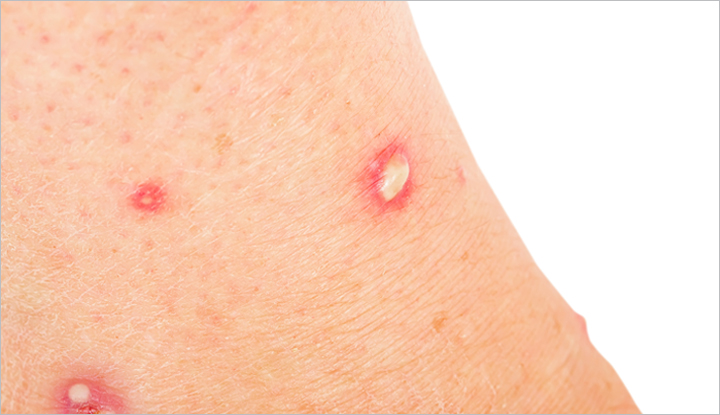
- Redness and Swelling: The immediate area around the bite usually becomes red and slightly swollen.
- Puncture Marks: Ants use their mandibles to bite, often leaving small puncture marks on the skin.
- Itching and Burning: The bite site can be intensely itchy and may feel like it’s burning, especially with certain species.
- Pustules or Blisters: Some ant bites, particularly those from fire ants, can develop into pustules or blisters.
The severity of the reaction varies depending on the ant species and individual sensitivity. For example, a bite from a common black ant might only result in mild irritation, while a fire ant bite can cause a severe, painful reaction.
Common Types of Ants and Their Bites
Different species of ants have varying levels of venom potency and bite characteristics. Identifying the type of ant responsible for the bite can help predict the severity of the reaction and guide treatment.
Fire Ants
Fire ants are notorious for their aggressive behavior and painful bites. Native to South America, they have spread to many parts of the world, including the United States, Australia, and parts of Asia. Fire ant bites are characterized by:
- Immediate Pain: The bite is instantly painful, often described as a burning sensation.
- Pustules: Within 24 to 48 hours, a white, fluid-filled pustule typically forms at the bite site.
- Clustered Bites: Fire ants often bite multiple times in a cluster, as they tend to swarm and attack together.
Fire ant venom contains alkaloids that cause the characteristic burning sensation and pustule formation. Allergic reactions to fire ant bites can be severe, requiring immediate medical attention.
Carpenter Ants
While carpenter ants are primarily known for their wood-damaging behavior, they can also bite. Carpenter ant bites are:
- Painful: Though not as venomous as fire ants, carpenter ants have strong mandibles that can inflict a painful bite.
- No Venom Injection: Carpenter ants do not inject venom during their bites, so the reaction is usually limited to the immediate area.
- Defensive Bites: They typically bite only when threatened or disturbed.
Harvester Ants
Harvester ants are known for their potent venom and painful bites. These ants are commonly found in dry, open areas. Harvester ant bites are:
- Intense Pain: The venom of harvester ants is more potent than that of fire ants, resulting in more severe pain.
- Localized Swelling: The bite site can become significantly swollen and red.
- Long-Lasting Effects: The pain from a harvester ant bite can last for several hours or even days.
Pavement Ants
Pavement ants are small, common ants that are frequently found in urban environments. Their bites are generally mild and cause minimal discomfort. Pavement ant bites are:
- Minor Irritation: The bites usually cause only slight itching and redness.
- Not Aggressive: Pavement ants are not typically aggressive and only bite when provoked.
- Quick Resolution: The symptoms usually resolve quickly without any specific treatment.
Treating Ant Bites
The treatment for ant bites depends on the severity of the reaction. Most ant bites can be managed at home with simple first aid measures. However, severe reactions require immediate medical attention.
Home Remedies
- Wash the Area: Gently wash the bite area with soap and water to remove any dirt or debris.
- Apply a Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or loratadine (Claritin), can help alleviate itching.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Applying a topical corticosteroid cream, such as hydrocortisone, can reduce inflammation and itching.
- Calamine Lotion: Calamine lotion can also help soothe the skin and relieve itching.
Medical Treatment
Seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms after an ant bite:
- Severe Allergic Reaction: Symptoms such as difficulty breathing, wheezing, dizziness, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue require immediate medical care.
- Signs of Infection: If the bite area becomes increasingly red, swollen, or painful, or if you develop a fever, it could indicate an infection.
- Persistent Pain: If the pain from the bite is severe and does not improve with home treatment, consult a doctor.
Medical treatments for severe ant bites may include:
- Epinephrine (EpiPen): For severe allergic reactions, an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) may be necessary.
- Oral Corticosteroids: Doctors may prescribe oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If an infection develops, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Preventing Ant Bites
Prevention is the best approach to avoid the discomfort and potential health risks associated with ant bites. Here are some effective strategies:
- Avoid Ant-Infested Areas: Be cautious when walking in grassy areas, parks, and other outdoor environments where ants are common.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When working outdoors, wear long sleeves, pants, and closed-toe shoes to minimize exposed skin.
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin to your skin and clothing.
- Keep Food Covered: Ants are attracted to food, so keep food covered and clean up any spills promptly.
- Seal Cracks and Openings: Seal any cracks or openings in your home to prevent ants from entering.
- Professional Pest Control: If you have a persistent ant problem, consider hiring a professional pest control service.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most ant bites can be treated at home, it’s essential to know when to seek medical attention. Watch for signs of a severe allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, wheezing, dizziness, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. These symptoms require immediate medical care. Additionally, if the bite area becomes increasingly red, swollen, or painful, or if you develop a fever, it could indicate an infection that needs medical treatment.
Conclusion
Ant bites, though often minor inconveniences, can sometimes pose serious health risks. By understanding how to identify different types of ant bites, administering appropriate treatment, and implementing preventive measures, you can effectively manage and minimize the impact of these encounters. Remember to seek medical attention when necessary to ensure prompt and effective care. Staying informed and proactive is the best way to protect yourself and your loved ones from the potential dangers of ant bites.
[See also: Insect Bite Identification Guide]
[See also: Managing Allergic Reactions to Insect Bites]
[See also: First Aid for Insect Stings]
